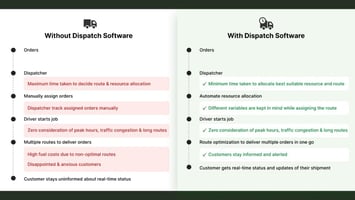
The landscape of delivery logistics is undergoing rapid evolution to keep up with the dynamic...
Logistics Glossary- OS1
The terminology used in the logistics sector is constantly evolving as the landscape is changing rapidly.

Let us take stock of some terminology that are highly relevant today and we hope this will serve as a ready reckoner for logistics professionals - both beginners and advanced.
Logistics Alphabetic Glossary
- A to E
- F to P
- R to Z
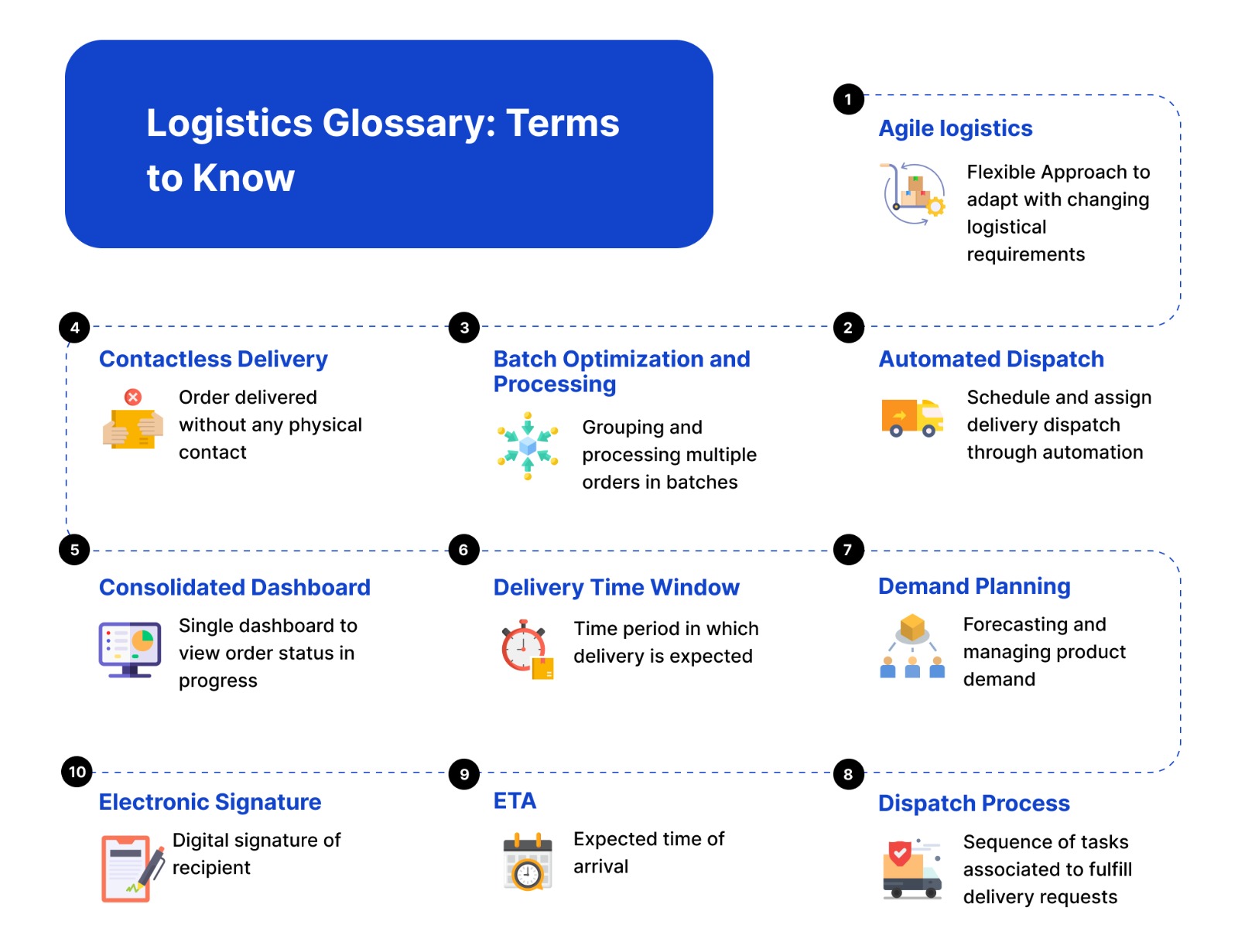
Here is a list of definitions to enhance your understanding of logistics concepts and terminology.
Logistics Terms: A to E
Agile Logistics
Logistics management needs to accommodate dynamic market requirements while planning a supply chain process. Agile logistics refers to real-time flexibility in response to unique and changing customer requirements.
Automated Dispatch
It refers to using automation in generating, scheduling, and assigning dispatch tasks to drivers and vehicles. As soon as an order is captured, automated dispatch accelerates the delivery process by creating a quick-to-execute dispatch plan.
Batch Optimization and Processing
Multiple orders received from different sources are processed and grouped into batches. Batch optimization and processing include efficiently adding incoming orders into different sets based on similar delivery routes and timing requirements.
Contactless Delivery
A process where a shipment is delivered to customers while ensuring no face-to-face or physical contact is made between the delivery person and the recipient. Often used for safety and hygiene reasons, contactless delivery is in high demand during and after pandemic times
Consolidated Dashboard
A single interface that showcases all the required information and data insights captured from various sources at different stages of the fulfillment process The dashboard provides a unified view of logistics operations, enabling dispatchers to make quick and informed decisions.
Delivery Time Window
A specified time slot is selected by customers while placing an order. Based on the opted time window by customers, a dispatcher needs to plan, schedule and allocate shipment delivery.
Demand Planning
Demand planning is an important aspect of supply chain management, where businesses forecast and strategically manage the expected demand for their products or services. The process involves analyzing historical data, market trends, and other factors to predict demand, helping businesses optimize their production, procurement, and distribution processes.
Dispatch Process
The dispatch process involves a series of tasks and activities through which an order is delivered to its recipient. It consists of scheduling, routing, and navigating drivers to ensure a streamlined delivery is made efficiently.
Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA)
ETA signifies the expected time for a shipment to reach its intended destination. Various factors, such as distance, speed, traffic conditions, and potential delays, are considered while ETAs for a specific shipment are calculated. A precise ETA helps reduce WISMO call frequency and drives a better delivery experience.
Electronic Signature
An electronic signature is a digital representation of a recipient's signature used to confirm and authenticate the shipment received. Electronic signatures are used in the logistics industry to streamline processes and efficiently confirm receipt or approval without traditional ink-and-paper signatures.

Logistics Terms: F to P
Failed Deliveries
It refers to situations where a delivery attempt is unsuccessful. It occurs often due to various reasons ,including the recipient not being available at the specified location, incorrect address information, errors in packaging or fulfillment, tracking issues and many more.
First Attempt Delivery Rates
The percentage of deliveries that are completed on the first delivery attempt without the need for reattempts. A higher first-attempt delivery rate helps drive a better customer experience and minimizes operational costs.
Field Operations
The tasks carried out by drivers on the field are called "Field Operations." Field operations often involve real-time communication, scheduling, and coordination to optimize workflow and deliver quality service.
Fulfillment Cycle
It encompasses the complete process, from receiving an order to delivering the shipment to the customer. It includes steps such as order processing, inventory management, order allocation, picking, shipping, and tracking of order status until it is delivered to the recipient.
Late Deliveries
Deliveries that are not completed within the initially promised or expected time frame are categorized as late deliveries.
Logistics management
It includes the process of planning, implementation, and control of the movement of goods and services to meet customer requirements efficiently. The primary goal of logistics management is to optimize these processes to ensure that orders are delivered on time while minimizing operational costs and maximizing efficiency. Effective logistics management plays a significant role in ensuring businesses remain competitive and adhere to promised SLAs.
Logistics operations
The day-to-day activities and processes involved in managing the flow of captured orders within a logistics network are categorized as logistics operations.
Omnichannel visibility
It refers to tracking and monitoring multiple order statuses in one place. Dispatchers can simultaneously experience a comprehensive and real-time view of incoming orders and orders in progress. It allows companies to manage operations more effectively, optimize delivery workflows, and provide a seamless and consistent customer experience across the fulfillment cycle.
Operational Cost
The expenses incurred in the day-to-day running of logistics and transportation operations is defined as operational cost.
Proof of Delivery
PODs are the written acknowledgment or evidence confirming a shipment's successful delivery to its intended recipient. It can be an electronic signature, OTP verification, or a live photo captured. It is an essential source of information in case of any delivery grievance or concern raised after delivery.
Payment Reconciliation
The process of verifying and aligning payments made and received within the logistics and supply chain ecosystem is termed payment reconciliation.
Peak Demand
"Peak demand" refers to the period when there is a significantly higher demand for a product or service compared to the usual or average demand levels. It occurs mainly in seasons, during specific events, or due to any other factors leading to a temporary surge in demand.
Performance Measures
Performance measures are metrics used for assessing and quantifying how effectively a delivery operation is executed. These metrics provide valuable insights into various performance aspects and help make informed decisions in the future.
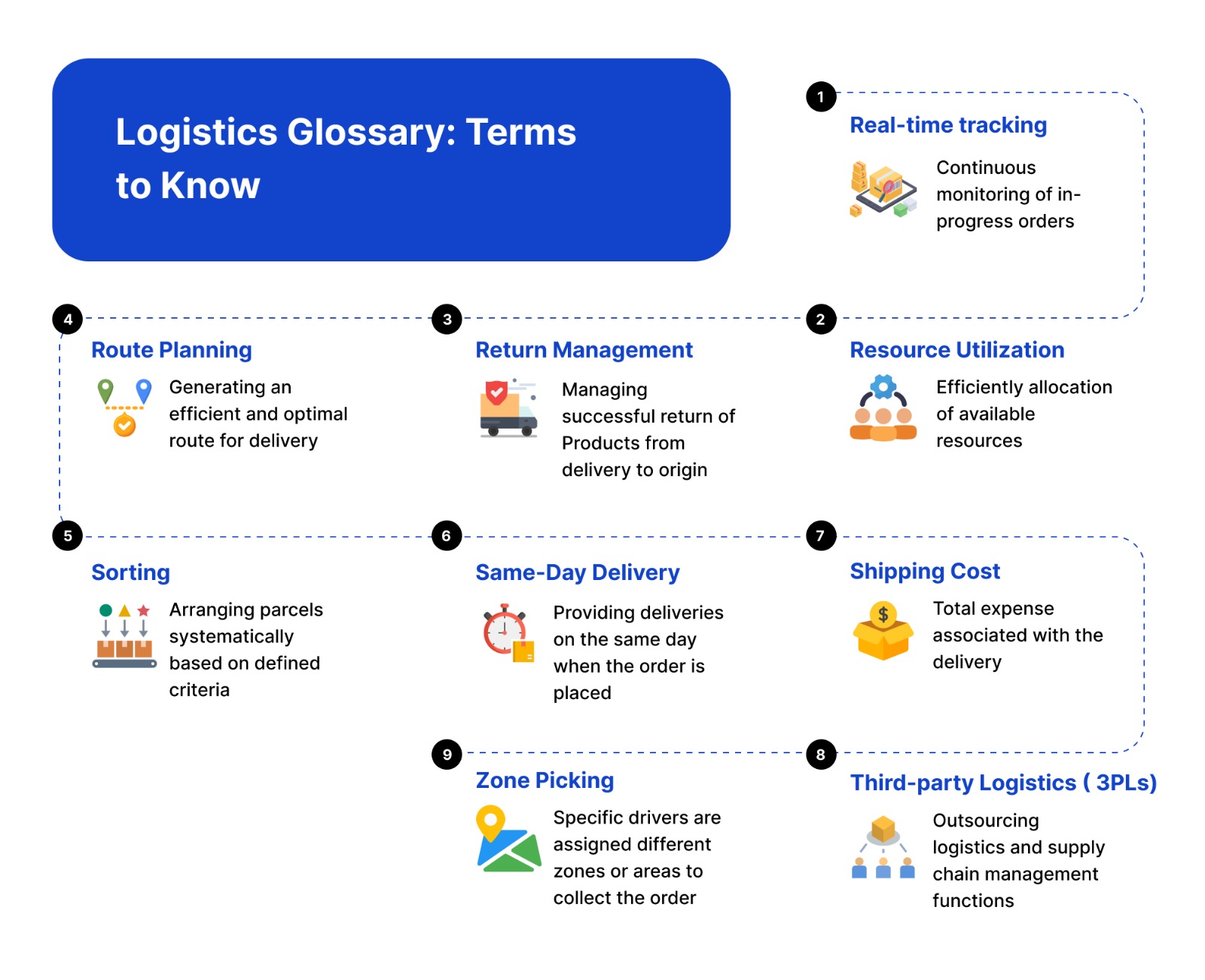
Logistics Terms: R to Z
Real time tracking
Real-time tracking refers to the continuous and immediate monitoring of the location, status, or progress of an order in progress. It helps identify any unexpected delivery disruptions and offers quick and proactive resolution to resolve them immediately.
Resource Utilization
Resource utilization refers to efficiently and effectively allocating available resources to accomplish tasks, projects, or objectives. Optimizing resource utilization involves ensuring that resources are used to maximize productivity, minimize waste, and achieve the desired outcomes.
Return Management
Returns management is a critical process in retail and e-commerce logistic operations. It begins when customers decide to return a product and concludes when the business successfully collects, organizes, and potentially restocks the returned items.
Route Planning
Route planning determines the most efficient and optimal route for delivery. The plan is generated considering various factors such as distance, travel time, traffic conditions, road restrictions, and the specific objectives of the journey.
Sorting
Sorting refers to the process of arranging items or products systematically based on specific criteria, such as size, category, destination, or other relevant factors. In logistics and distribution, sorting is often used to prepare goods for shipment and streamline the order fulfillment process.
Same Day Delivery
Same-day delivery is a service that offers delivery of goods or services to customers on the same day the order is placed. It's often used for time-sensitive or urgent deliveries.
Shipping Cost
It refers to the total expense associated with the delivery of orders during the complete fulfillment cycle. Transportation fees, packaging materials, and handling charges are included in calculating the overall shipping cost.
Third-party Logistics ( 3PLs)
Third-party logistics refers to outsourcing logistics and supply chain management functions to a third-party service provider. These providers offer services such as transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and distribution on behalf of businesses.
Zone Picking
Zone picking is used in warehouse operations where specific drivers are assigned different zones or areas to collect the order. Each driver or delivery agent is responsible for selecting items only from their designated zone, streamlining the order-picking process.
This is not the end. There’s more coming soon.
The logistics industry is undergoing significant growth and transformation, primarily driven by technological advancements. In the above sections, we've added various terms and keywords frequently used in the industry. Click here to stay updated with new additions in the logistics glossary.
If you're interested in delving deeper into these logistics concepts, feel free to get in touch with our experts.